INTRODUCTION
In today’s competitive environment, Trade Mark protection has become pivotal for every business. Safeguarding a trademark in India involves the below-mentioned procedures and legal requirements. This guide provides an extensive, step-by-step process to protect a trade mark.
UNDERSTANDING TRADE MARKS
Before discussing the protection process, it’s important to have a clear understanding of trade marks. A trade mark can be a word, symbol, design, or a combination of these elements that distinguishes the goods or services of one proprietor from those of its competitors. It serves as a valuable asset for businesses, helping consumers recognize and associate products or services with a particular brand. Not getting a trade mark registered can have detrimental effects, you can read about the same in detail on https://trialstrust.com/detrimental-effects-of-not-getting-a-trademark-registered-intellectual-property-law/
IMPORTANCE OF PROTECTING TRADE MARK
Protecting the trade mark from unauthorised use is essential to safeguard the brand’s integrity and reputation. By obtaining exclusive rights for the trade mark, others can be prevented from using similar marks in a way that can confuse consumers or dilute the brand’s distinctiveness. This protection extends to various aspects, such as logos, product names, and even packaging designs. Failing to protect your trade mark could lead to potential loss of business and brand value.
STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE TO PROTECT TRADE MARK
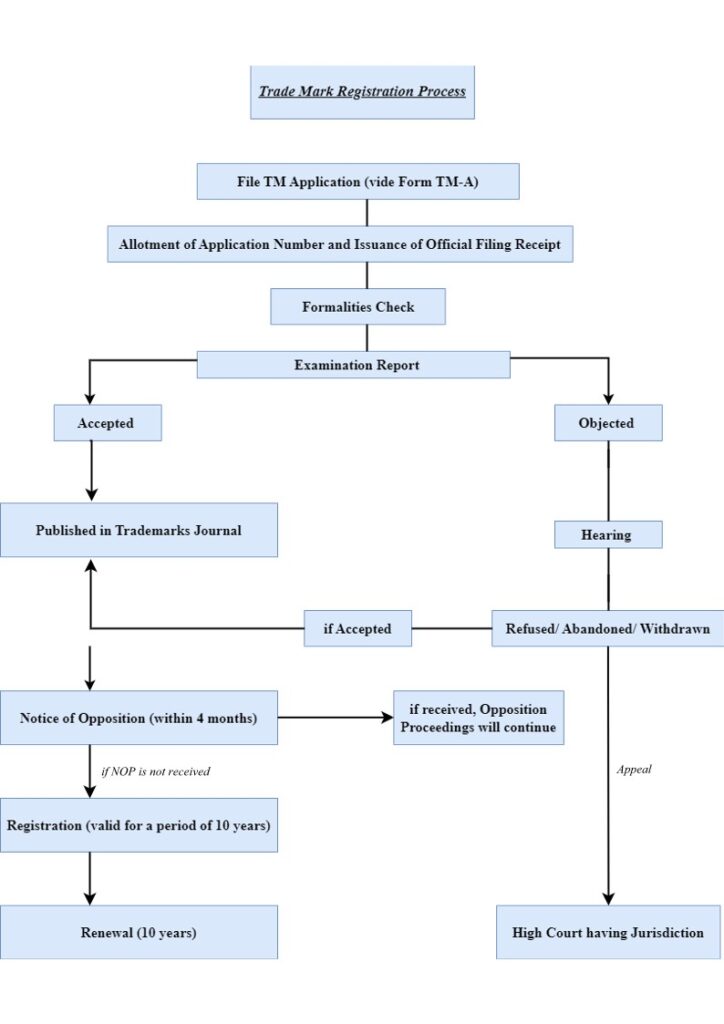
A. CONDUCTING A TRADE MARK SEARCH
Before filing a trade mark application, it’s necessary to conduct a comprehensive search to ensure that the intended mark is not already in use by any other proprietor. The search helps in identifying potential conflicts with existing trademarks and allows to make informed decisions about getting it registered.
B. FILING A TRADEMARK APPLICATION
After trade mark search, once it is determined that the intended trade mark is available, the next step is to file a trade mark application with the IPO, also known as the Office of the Controller General of Patents, Designs, and TradeMarks (CGPDTM). The application should include the details of the applicant, trade mark, its intended use, and the specific goods or services it will represent.
C. EXAMINATION AND PUBLICATION OF THE TRADE MARK
After filing the application, the trade mark office examines the mark to ensure that it complies with all the necessary requirements. Upon acceptance, the mark is published in the Trade Marks Journal, opening it up for potential opposition.
D. OPPOSITION PROCEEDINGS
After publication, third parties have the opportunity to oppose the registration of the trade mark if they believe that it conflicts with their existing rights. The time frame for opposing the mark is four months. If an opposition is filed, the matter will be adjudicated by the trade mark office, and both the parties will have a chance to present their respective cases.
E. REGISTRATION AND RENEWAL OF TRADEMARK
If no opposition is raised or if the opposition proceedings are successfully overcome, the trade mark will be registered. It’s important to note that trade mark protection is not indefinite and requires periodic renewal to maintain its legal force. The mark has to be renewed every ten years.
CONCLUSION
Safeguarding the trade mark involves a series of steps aimed at securing exclusive rights to the brand identity. By following the above-mentioned step-by-step guide, you can navigate the process of protecting the trade mark in India and ensure long-term value for your business.
If you wish to know more about Intellectual Property, kindly visit the below-mentioned links – (i) https://trialstrust.com/what-is-intellectual-property-ip/ ,(ii) https://trialstrust.com/india-registering-protecting-trade-marks-ip-law/ ,(iii) https://trialstrust.com/clearing-five-misconceptions-about-trade-marks-trade-marks-myths-intellectual-property-law/ …
You can connect with us on – https://www.instagram.com/trialstrust/?igsh=NDZpdDN2ZjY4bXc4&utm_source=qr
Tags:
#copyrights, #intellectualproperty, #IPinIndia, #patents, #Intellectual Property Rights, #TRADE MARK, #trademark, #trademark registration process, #TRADEMARKS, #IPIndia