Introduction
In today’s globalized world, Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) play a crucial role in protecting the creations and innovations of individuals and companies. One such form of Intellectual Property is trade mark, which serves as a unique identifier of goods or services. Registering and protecting trade marks in India is a vital step for businesses looking to establish their brand identity and prevent unauthorized use. In this article, we will explore the significance of trade mark registration and the procedure for protecting trade marks in India.
Importance of Trade Mark Registration
Trade Mark registration provides legal protection and exclusive rights to the owner, preventing others from using identical or similar marks for similar goods or services. It helps businesses establish a distinctive brand identity, builds customer trust and enables effective marketing and advertising campaigns. Registering a trade mark also serves as an evidence of ownership, facilitating legal action in case of infringement.
Process of Trade Mark Registration in India
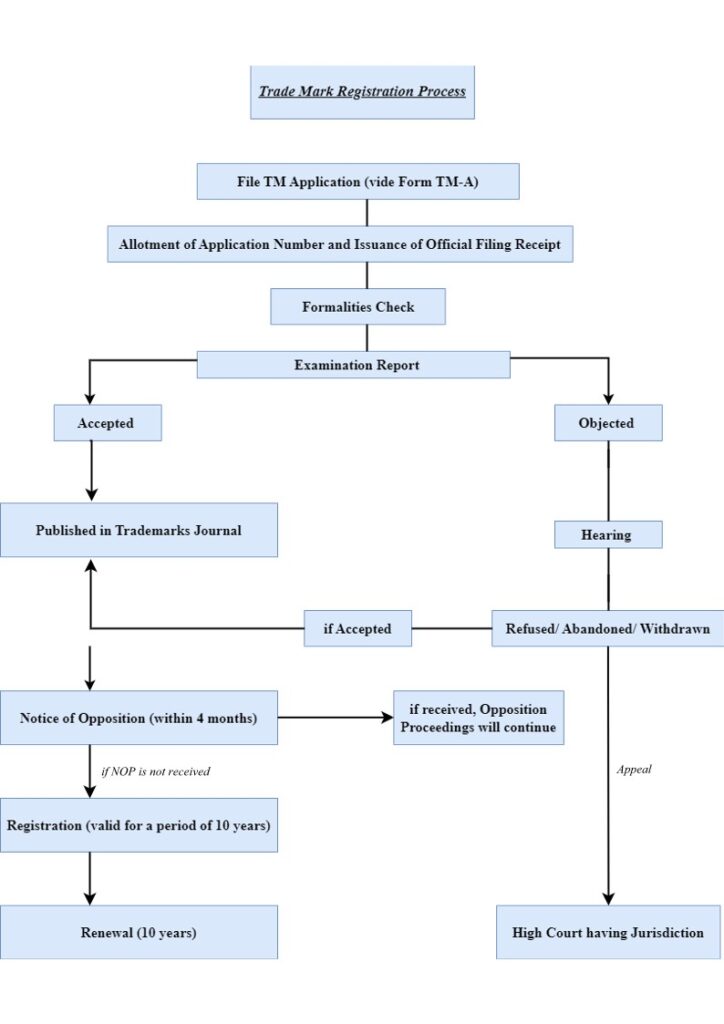
The above chart shows the Trade Mark registration process in a nutshell. Let’s understand it in brief for a better clarity –
- Trade Mark Search: Before applying for registration, it is essential to conduct a thorough trade mark search to ensure that a similar mark is not already registered or pending for registration. This search can be done online through the official Trade Marks Registry website.
- Filing the Application: Once the search is complete, the next step is to file the trade mark application with the Trade Marks Registry. The application should include the desired mark, the class of goods or services and the name, address, and nationality of the applicant.
- Examination and Publication: After filing, the Trade Marks Registry examines the application for compliance with the legal requirements. If no objections are raised, the mark is published in the Trade Marks Journal for public scrutiny. Any interested party can oppose the registration within a period of 4 months.
- Opposition Proceedings: If an opposition is filed, both the parties are given an opportunity to present their arguments and evidence before the Registrar. The Registrar will then decide whether the mark should be registered or rejected.
- Registration and Renewal: If the application is accepted and no opposition is raised, the mark is registered, and a certificate of registration is issued. In India, trade mark is valid for a period of ten years from the date of application and can be renewed indefinitely.
Protecting Trade Marks in India
Once a trade mark is registered, it is important to actively protect it from infringement to maintain its exclusivity. Here are some measures businesses can take to safeguard their trade marks:
- Monitoring: Regularly monitor the market for any potential infringements or unauthorized use of the registered mark. Promptly identify and take legal action against infringing parties to protect your rights.
- Enforcement: If you discover infringement, consult an intellectual property lawyer to understand your legal options. This may include sending cease and desist letters, initiating legal proceedings, or claiming damages for the unauthorized use of your trade mark.
- International Protection: Businesses planning to expand globally should consider registering their trade mark in other countries as well. This will provide protection in those jurisdictions and prevent others from using your mark.
Conclusion
Registering and protecting trade marks in India is a crucial step for businesses to establish their brand identity and prevent unauthorized use. By understanding the importance of trade mark registration and following the necessary processes, businesses can ensure the exclusivity and legal protection of their trade marks. By actively monitoring and enforcing their rights, businesses can safeguard their intellectual property and secure a competitive edge in the market.
kindly connect with us on https://www.instagram.com/trialstrust?igsh=NDZpdDN2ZjY4bXc4&utm_source=qr
TrialsTrust
Table of Contents
Proudly powered by WordPress